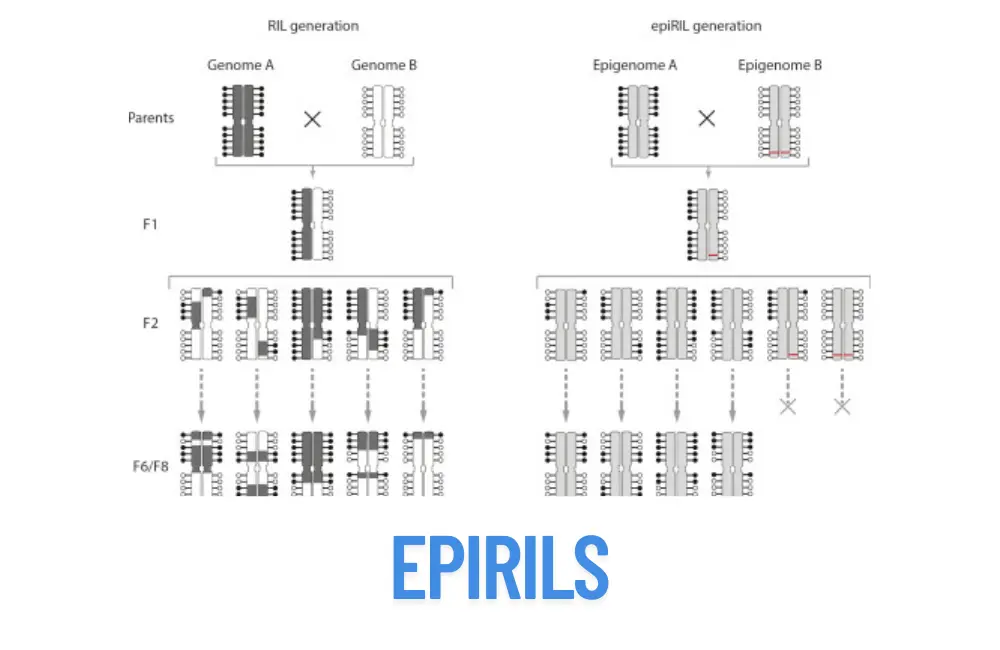
Examine the function of epirils epigenetic recombinant inbred lines in plant breeding and genetics.
How Does Epirils Operate and What Is It?
Ramipril, the main ingredient in epirils, is a potent drug that is a member of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class. It is mainly used to treat congestive heart failure, hypertension (high blood pressure), and to increase heart attack survivor survival. By relaxing blood arteries, epi rils lessen the strain on the heart and aid in improved blood pressure control by facilitating the heart’s ability to circulate blood efficiently.
This medication is essential for preventing heart attacks, strokes, and renal issues, especially in individuals who are at risk for cardiovascular disease or diabetes. It works by preventing the molecule angiotensin I from being converted to angiotensin II, which narrows blood vessels.
Uses of Epirils in Medicine
1. High blood pressure, or hypertension
The risk of renal failure, heart disease, and stroke is greatly increased by high blood pressure. By widening the arteries and lessening the burden on the heart, epirils successfully decreases blood pressure. It is therefore a crucial part of managing hypertension over the long run.
2. Heart Failure with Congestive Heart Failure
Epirils helps patients with heart failure because it increases cardiac output and decreases fluid retention. In patients with left ventricular dysfunction, it enhances symptom management, lowers hospitalization rates, and raises survival rates.
3. Treatment for Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
After a heart attack, epi rils is frequently administered to lower the risk of more cardiac episodes. After a major cardiac event, it aids in preventing ventricular remodeling, a process that might result in heart failure.
4. Diabetes and Kidney Protection
Epirils can slow down the progression of kidney damage in diabetic patients, particularly those who have microalbuminuria or proteinuria. It helps avoid diabetic nephropathy by regulating blood pressure and renal strain.
The Administration and Dosage
Tablets of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg of epi rils are available in different strengths. The patient’s age, general health, and particular condition all affect the dosage. For hypertension, a standard starting dose is 2.5 mg once daily. This can be increased gradually to 10 mg once daily, either in one dose or in two doses.
Lower initial doses are used to reduce the risk of side effects in individuals with heart failure and those who have had a MI. Following the doctor’s prescription is essential; do not self-medicate or change dosages without first consulting a doctor.
Possible Adverse Reactions to Epirils
Despite being typically well tolerated, epi rils may have some adverse effects, some of which may necessitate medical intervention.
Typical adverse effects:
- Cough (persistent and dry)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Nausea
Serious Adverse Reactions:
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema)
- Severe abdominal pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Jaundice or liver problems
- Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels)
- Kidney dysfunction
Immediate medical attention should be sought if angioedema or allergic reactions occur.
Safety Measures and Caution
1. Lactation and Pregnancy
Because of the possibility of fetal harm or death, epirils should not be used during pregnancy, especially during the second and third trimesters. When taking epi rils, women of reproductive age should utilize an effective form of contraception. Avoiding epi rils while nursing is also advised.
2. Individuals with impaired kidney function
Careful monitoring of renal function is necessary, particularly in patients who already have kidney disease. Epirils may raise potassium or creatinine levels, necessitating dose changes or stopping the medication.
3. Interactions with Drugs
A number of drugs may interact with epi rils, including:
- Diuretics
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen)
- Potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics
- Lithium
- Antidiabetic drugs
These interactions can lead to serious side effects such as electrolyte imbalance, kidney damage, or hypotension.
Epi Rils Advantages Compared to Other ACE Inhibitors
Because of its long-lasting effectiveness, reduced risk of adverse effects, and greater tolerance, epirils can be used once daily. Because of its shown effectiveness in preventing diabetic kidney damage and long-term cardiovascular protection, it is frequently preferred over other ACE inhibitors.
Observing When using Epi Rils
To guarantee safety and effectiveness, patients taking epirils need to be regularly monitored. This comprises:
- Blood pressure readings
- Renal function tests (creatinine, BUN)
- Serum potassium levels
- Liver function tests
Regular follow-ups help in adjusting dosage and preventing complications.
Lifestyle Recommendations While Taking Epirils
To maximize the effectiveness of epirils, patients should adopt a healthy lifestyle, including:
- Low-sodium diet
- Regular physical activity
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking
- Stress management
- Weight control
These practices, in conjunction with epi rils, significantly enhance heart and kidney protection.
Who Should Not Take Epirils?
Epirils should not be taken by individuals who:
- Have a history of angioedema
- Are pregnant or planning pregnancy
- Have severe kidney impairment
- Are allergic to ramipril or other ACE inhibitors
- Have bilateral renal artery stenosis
FAQs
1. What sets Epi RILs apart from conventional RILs?
The study of heritable epigenetic variation is made possible by the distinction between epirils and conventional Recombinant Inbred Lines (RILs), which differ in their epigenetic composition but share comparable genetic sequences.
2. What role do Epi RILs play in breeding initiatives?
Breeders can select for desired qualities by finding the epigenetic markers linked to such traits, which could result in enhanced crop types.
3. Is it possible to undo epigenetic modifications?
While certain epigenetic changes can be permanently inherited, others can be reversed. The type of change and environmental conditions determine the reversibility.
4. Do all plant species benefit from Epi RILs?
Although the idea of epirils was first created in Arabidopsis thaliana, it can be extended to other plant species, however the complexity of creating and studying such lines may differ.
5. What resources are employed to investigate epigenetic modifications in EpiRILs?
Epigenetic changes in epi rils are frequently analyzed using methods such as RNA sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and bisulfite sequencing.
Conclusion
Epirils has solidified its standing as a key treatment for the treatment of renal and cardiovascular diseases. It is a multipurpose and essential drug because of its capacity to reduce blood pressure, enhance heart health, and safeguard kidney function. Its long-term use can greatly assist patients with proper monitoring, dosage management, and lifestyle changes.












Leave a comment