Biometric technology is no longer confined to the realm of blockbuster science fiction movies.
From your smartphone to international airports, it has become the new standard for proving our identity. And nowhere is this transformation more apparent than in the government, as more and more national ID programs begin to benefit the security, speed, and trust in public services from biometric systems.
Why Governments Are Embracing Biometrics
Physical ID cards, passwords, and PIN numbers can be lost, stolen, or replicated with relative ease. Biometrics, on the other hand, are comprised of unique human traits (like irises or fingerprints) that are much more difficult (if not impossible) to replicate.
For counties with millions of residents, a biometric system for national ID ensures accuracy and safety during the registration process. It also helps countries provide services to their citizens like healthcare, benefits payouts, and voting without any duplication or fraud.
The Enrollment Stage: Where It All Begins
Strong ID systems start with the process of accurate enrollment. This is where the typical fingerprint reader and its related biometric-capture equipment are indispensable. If the input data is inaccurate or nonexistent, then even the most sophisticated database won’t help.
Suppliers of fingerprint readers and other biometric devices for use in an ABIS system are designed to handle the wear and tear of government programs. Accurate data capture is the cornerstone of a trusted ID infrastructure.
ABIS: The Engine Behind the System
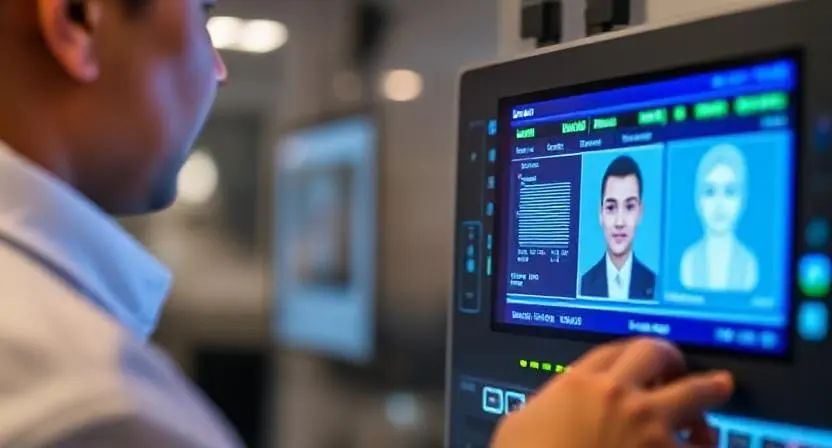
Once citizens are signed up, it’s necessary to manage and verify the thousands or millions of identity records. This is the role of the automated biometric identification system (ABIS).
ABIS can handle fingerprints, faces, irises, and even voice. Its powerful algorithms search large biometric databases exceptionally quickly, making it especially important for national ID projects.
This flexibility empowers governmental bodies to deploy a single system that accommodates population growth. It also guarantees that each citizen’s biometric identity is one-of-a-kind and kept secure.
Beyond Identification: The Wider Impact
There is much more to biometric ID than identity. Here is a selection of how this tool can affect other sectors:
- Financial inclusion: those lacking conventional documentation can bank or make digital payments.
- Healthcare: record automation via unique ID curbs time wastage and fraud.
- Borders: biometrics strengthen immigration, limiting illegal crossings.
But for business, the attraction of biometrics is also obvious. Banks, telecoms, and e-commerce all experience efficiency and security boosts through swifter customer ID.
Addressing Security and Trust
Of course, the idea of a national biometrics database immediately sparks alarm. What’s to stop security forces or emboldened bureaucrats from using the information to track down political activists, crush dissent, or persecute religious or ethnic minorities? What if the data, perhaps stored in a central database, is hacked, stolen, or sold to unscrupulous actors? What if competing foreign powers could tap into a country’s biometric database for their own nefarious purposes?
Even an advanced ABIS platform will certainly face an immediate public backlash without transparency and accountability.
The Future of National ID Systems
As technology improves, multimodal biometrics will allow for the use of multiple biometric modalities, such as fingerprint, face, iris, and voice, at the same time. This increases accuracy and decreases errors.
Strong enrollment capabilities and matching engines indicate a future for national ID systems where they will get faster, safer, and more inclusive.
Conclusion
Biometric systems are actively streamlining processes around the globe and making countries’ national databases more curated. From confirming our live presence using fingerprint readers to matching a million fingerprint templates in one second with ABIS, each of these technologies is a step closer to creating a secure national database.
If a country is investing in digital governance, a biometric national ID system is not an option but a considerable aspect of creating a safer, efficient, and transparent society.













Leave a comment